
Floating wind power offers enormous potential for deepwater offshore energy development. However, the management and secure exchange of data between stakeholders represents a key challenge for its evolution. A new cryptographic framework, proposed by researchers Claudia Bartoli (IMDEA Software) and Irene Rivera-Arreba (Norwegian University of Science and Technology, NTNU), presented at WindTech 2024 Conference, tries to solve this problem with a data sharing scheme that guarantees data integrity without compromising privacy. This breakthrough seeks to foster collaboration between industries and academia, driving innovation in floating wind technologies.
Context
Floating wind power is positioned as a promising frontier in the renewable energy sector, enabling the expansion of offshore wind power to areas of greater depth. To harness this potential, it is essential to share reliable data between parties such as companies and academics.
Access to datasets is crucial at all stages of development, from site selection to maintenance. In addition, sharing data fosters innovation, attracts investment and strengthens trust among stakeholders. However, handling large volumes of data and protecting intellectual property pose significant challenges.
The current approach relies on data certified by certification bodies (Certification Body), but these often lack critical details to optimize system performance. In response, the researchers have described a cryptographic protocol that enables the secure exchange of critical data, ensuring privacy and integrity through advanced tools such as zero-knowledge proofs.
The study
The protocol proposed by Bartoli and Rivera-Arreba has been designed to facilitate interactions between the various parties involved in offshore wind energy development. It has the potential to transform data sharing in the wind energy sector, improving collaboration between industry and academia since it ensures data integrity between parties without disclosing additional information. With the implementation of this protocol, “Through the use of techniques such as Multi Party Computation (MPC), this approach allows the analysis of encrypted data, ensuring the confidentiality of the information while sharing the results obtained by such analysis” assures Claudia, lead researcher of the article.
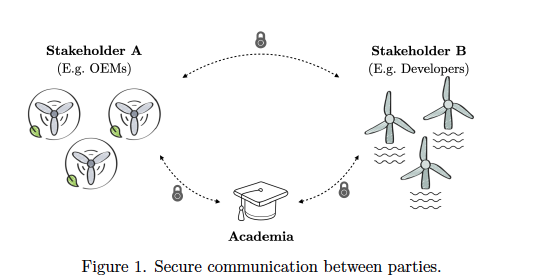
In addition, the system incorporates cryptographic signatures and succinct commitment schemes to reduce costs and facilitate the management of large databases. These innovations open up new possibilities to overcome current limitations in data availability without compromising data privacy.
Conclusion
The implementation of this cryptographic protocol could mark a step forward in the development of floating wind power. By enabling the confidential exchange of data, it fosters innovation and contributes to bridging the gap between privacy and availability. This breakthrough represents a promising solution to address technological and regulatory challenges on the road to a sustainable future in the renewable energy sector and paves the way for future research in this regard.
https://virtual.oxfordabstracts.com/event/32109/submission/134